The vast expanse of the high seas is facing unprecedented threats. Overfishing, pollution, and climate change are pushing marine ecosystems to the brink. But there’s hope. The High Seas Treaty offers a critical opportunity to safeguard the health of our ocean and the incredible biodiversity that call the ocean home.
What is the High Seas Treaty?
The road to ratification: Your voice matters
For the High Seas Treaty to become law, it must be ratified by at least 60 countries. Only 5 countries have ratified the Treaty so far- there are 55 to go! Recently, the EU has voted to ratify the treaty, which could fast track the ratification process for the 27 EU countries before the 2025 UN Ocean Conference.
By signing our petition, you’ll join a growing movement urging your government to ratify the High Seas Treaty by the end of 2025.
Your voice matters. Together, we can send a powerful message to our leaders, highlighting the urgency of protecting our shared oceans.
Why is the High Seas Treaty important?
The high seas are teeming with life, from microscopic plankton to majestic whales. These ecosystems play a vital role in regulating our planet's climate, producing half the oxygen we breathe, and absorbing a quarter of the carbon dioxide we emit.
However, the lack of regulations in international waters means the ocean is in crisis, caused by a few key drivers:
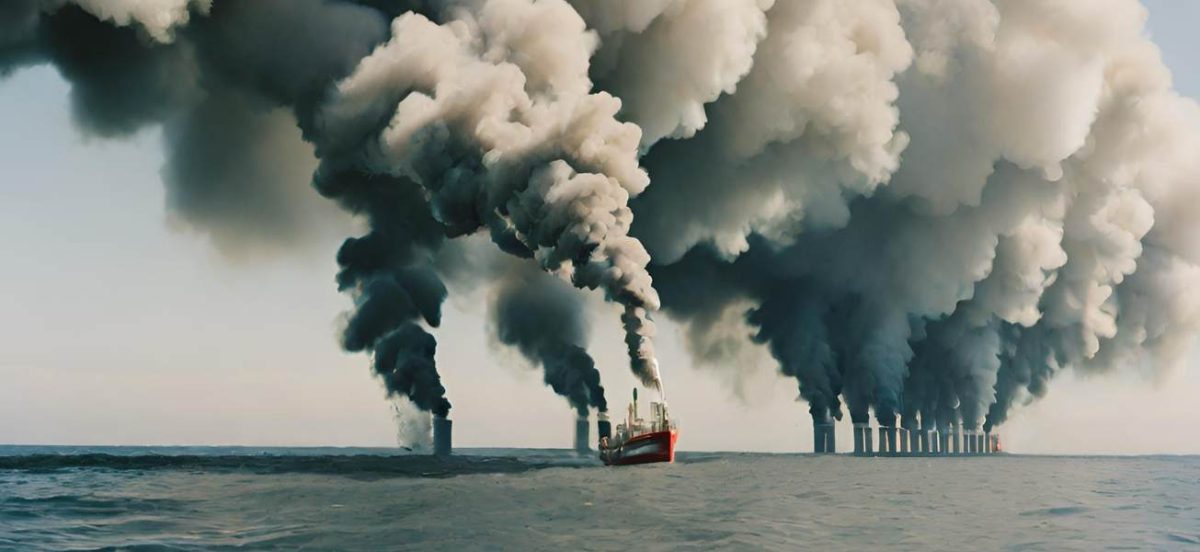
Increased greenhouse gas emissions
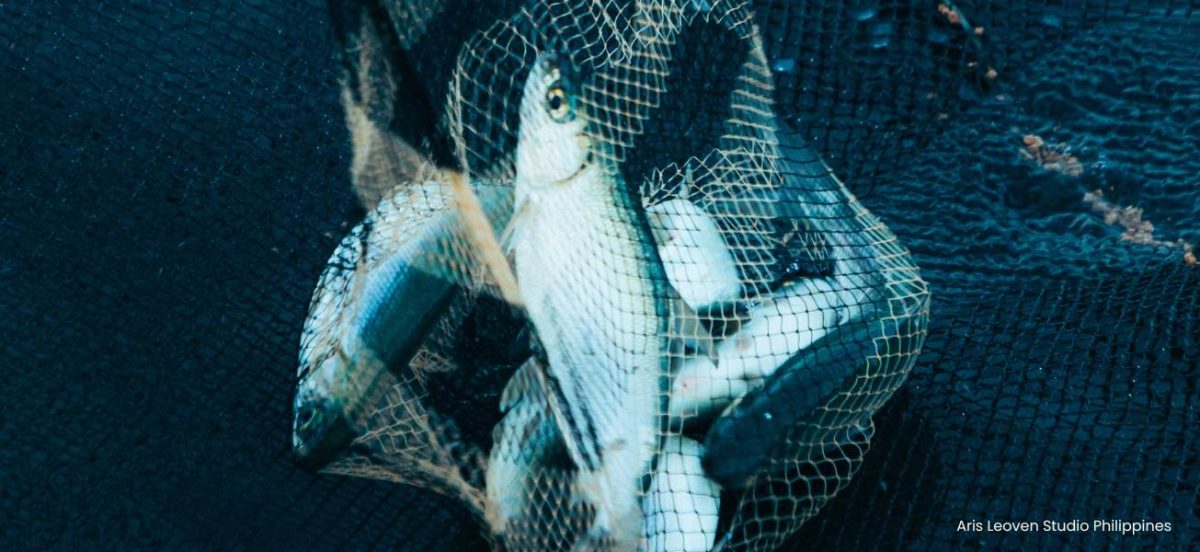
Overfishing
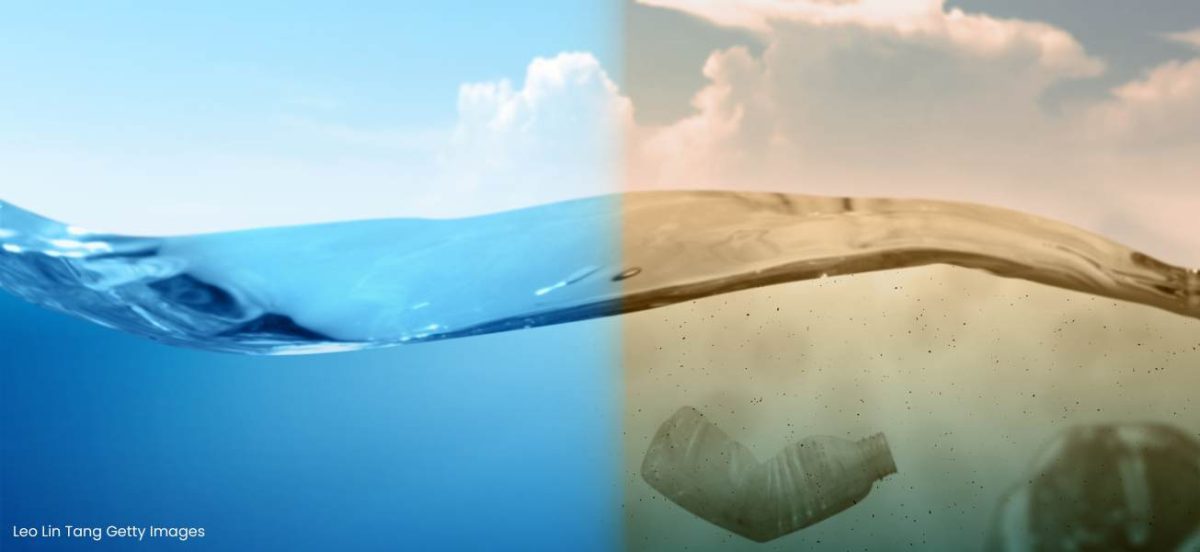
Chemical, noise and plastic pollution
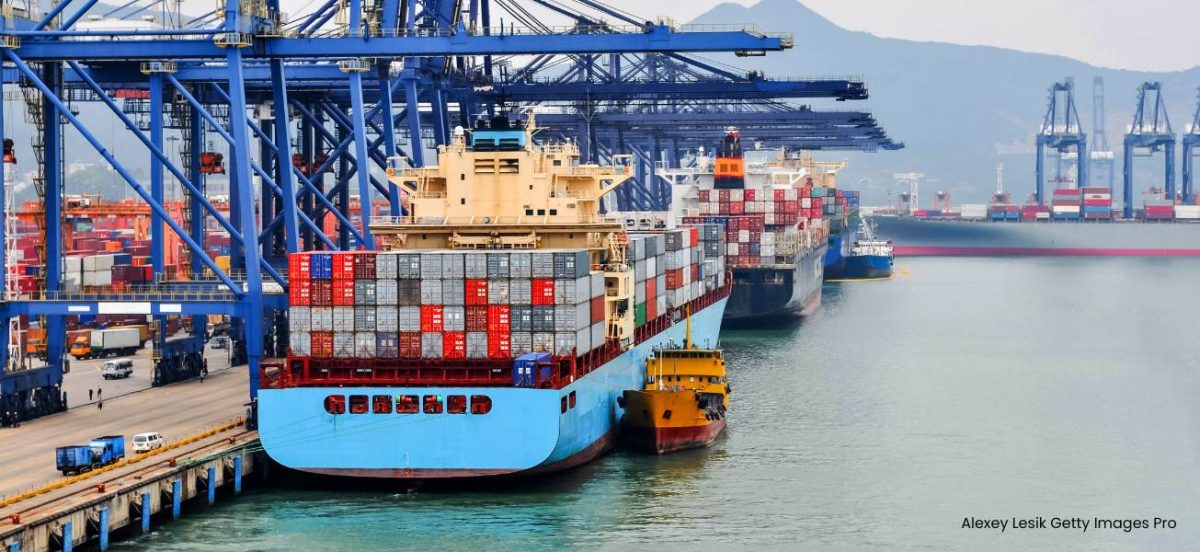
High shipping volumes
The High Seas Treaty: A powerful way to protect the ocean
The High Seas Treaty provides a framework for the following